Home
Environmental Geology: Geologists investigating our environment
Ecology and Geology: The interplay between the animate and the physical
The mission of a Geologists is to investigate the great variety of earth processes and earth systems including:
 |
|
Quartz: Image by Smith Clark, Smithzonian |
Composite Volcano: Image by Lee Siebert, Smithzonian
Phacops (Trilobite) from Silica Shale, Sylvania Ohio: Image from by Extinctions.com |
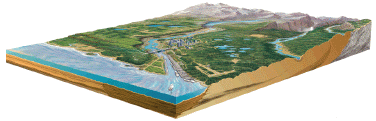
Environmental geology is the study of the interactions between the environment and the underlying geology as well as the impact of humans on the environment. In this field of geology, a scientist can investigate the degree of impact contamination has on the environment as well as the characteristics of the contamination and how to remediate (clean up) the contamination. This area of specialty is known as geochemistry. A geochemist uses geology and chemistry to study the environment and the effects of contamination. Another area of environmental geology known as hydrogeology is the study of groundwater and its relationship with the underlying geology. In the case of contamination, a hydrogeologist studies the transport of contamination by groundwater movement through the subsurface.
Image from USGS (http://water.usgs.gov/pubs/circ/circ1139/index.html)
To Top
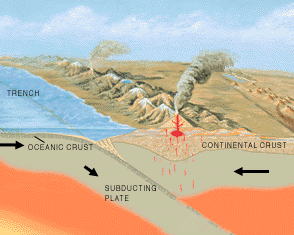
Ecologists play a crucial role in environmental investigations. While geologists largely investigate the inanimate component of our environment, ecologists investigate the living component including the interaction of ecosystems with the geological substrate. This interaction acts both ways: ecological processes often work in concert with geological (physical) processes to shape the earth and, at the same time, geological processes often exert strong controls on the types of biological communities that thrive in an area.
Image from USGS by Robert Meade (http://water.usgs.gov/pubs/circ/circ1139/index.html)