Department of Environmental Sciences, Mail Stop 604, University of Toledo, 2801 West Bancroft St.,Toledo, OH 43606-3390
General Course Syllabus
Physical Geology, EEES-1010, 3 credit hours
(Offered
Monday-Wednesday-Friday or Tuesday-Thursday, Morning or Afternoon)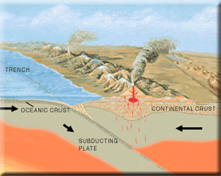
Course Objective: By investigating earth's materials, processes and features we learn that our planet is dynamic and continuously changing. With an understanding of the materials that comprise the earth, we then focus on the processes that continually shape and reshape the landscape and the earth's interior. This knowledge is used to understand geologic history, distributions of geologic resources, geologic hazards, and environmental impacts of humans.
 Accompanying
Laboratory Course: EEES-1020, 1
credit hour, is an optional laboratory course which follows the outline for
this lecture course. This companion
course focuses on mineral and rock identification, map reading, and analysis of
geologic structures. The student is not
required to take both courses, nor do both courses have to be taken
simultaneously. However, you will find
the visual and "hands on" nature of EEES-1020 very helpful for
understanding the material in this course.
Accompanying
Laboratory Course: EEES-1020, 1
credit hour, is an optional laboratory course which follows the outline for
this lecture course. This companion
course focuses on mineral and rock identification, map reading, and analysis of
geologic structures. The student is not
required to take both courses, nor do both courses have to be taken
simultaneously. However, you will find
the visual and "hands on" nature of EEES-1020 very helpful for
understanding the material in this course.
General Course Schedule
Week
1 - Introduction to Geology: Environmental geology, geologic hazards, geologic history, and careers in geology
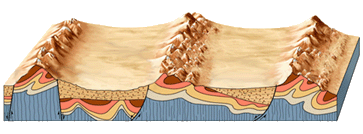
2 - Introduction to Plate Tectonics: Formation and structure of the earth, continental drift, tectonic forces shaping the earth's surface and interior
3 - Minerals: Crystal chemistry, crystalline structure, common rock forming minerals, ore minerals and gems
4 - Igneous Rocks: Where rocks melt, crystallization of magma, granite, basalt and exotic igneous rocks
5 - Volcanoes: Types of lava and eruptions, formation of volcanoes, fissure eruptions, basalt floods, submarine volcanism
6 - Weathering and Soil: Disintegration of rock, formation of sand, clay and soils
7 - Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks: Erosion, transport and deposition of sediments, formation of rock from sediment, clues to the environment of formation, and reading the earth's history stored in the rocks
8 - Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks: Earth's pressure cooker, "cooked rocks", minerals and rocks formed at increasing temperatures and pressures, and investigating the core of ancient mountain chains
9 - Geologic Time: Deciphering "deep time" of earth's history, the story of evolution preserved in earth's rocks, mass extinctions, braciopods, trilobites, fishes, dinosaurs, and mammals, relative age, and radiometric age dating.
10 - Mass Wasting and Streams: Water and gravity shaping the land, the water cycle, erosion, landslides, floods, and stream shaped landscapes
11 - Groundwater: The unseen part of the water cycle, aquifers, karsts, caverns, sinkholes, and dripstone, water resources and contamination
12 - Glaciers, Ice ages and Glacial Landscapes: Flowing ice carving landscapes, ice sheets, valley glaciers, global climate change
13 - Earthquakes: Evidence of an active earth
14 - Geologic Structures: Forces shaping the earth's interior